What is Long Range Forecast? It’s History & Background
The below article gives the information about:
History & Background of Long Range Forecast (LRF)
What is Long Period Average (LPA)?
Various Long Range Forecast for Monsoon Rainfall
What is Ensemble Statistical Forecasting System?
Monsoon Rainfall category for LRF
History & Background of Long Range Forecast (LRF):
- In 1877 there was a severe drought and famine condition all over India. The need was felt to estimate the prospective rains. So the first Chief Reporter of India Meteorological Department (IMD), was called upon to make long range forecast attempt.
- In 1892, long range forecast (LRF) for the rainfall for the second half of the monsoon season (August-September) was also started.
- In December 1893, for first time winter forecast precipitation over the Central and Northern India was issued.
- Sir Gilbert Walker who was D.G. of IMD from 1904 to 1924, started the forecasts based on objective techniques.
Before reading the Long Range forecast here are some terms and information need to be understood.
What is the LPA?
LPA is Long Period Average of rainfall taken for particular period of time. For example IMD consider LPA as a whole for the period 1951-2000 as 889 mms.
How LPA value is calculated?
LPA as term suggest, it is average of all the sub divisions in India. (Refer the figure below).
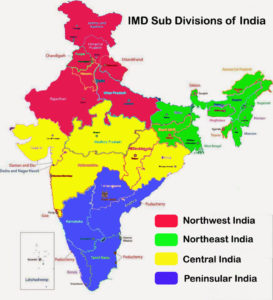
Various Long Range Forecast for Monsoon Rainfall:
IMD provides LRF and update it periodically. Below the period during which it provides the update for Monsoon Rainfall:
- All India Average Rainfall including all sub divisions: April
- Update for All India Rainfall Sub division wsie: June
- All India Second Half of Season for August-Sept Rainfall: July
- All India Monthly for September Rainfall: August
Since many years IMD is giving LRF based on Statistical Method using 100 years data. IMD is working to provide forecast with new system known as Dynamical forecasting. Dynamical forecasting uses the vast data of current atmospheric, oceans and even cloud conditions. But there are certain drawbacks using Dynamical forecast, to predict long range rainfall for monsoon.
- In 1988, IMD introduced the 16 parameter power regression & parametric model.
- After the failure of forecast in 2002, IMD introduced a new two stage forecast strategy by which the first stage of forecast is issued in April and updated for the April forecast is issued in June.
- In 2007, IMD introduced new statistical forecasting system based on ensemble technique for the southwest monsoon season rainfall over the country as a whole. In the ensemble method, instead of relying on a single model, all possible models based on all the combination of predictors are considered.
What is Ensemble Statistical Forecasting System?
IMD using the model for LRF is based on the Ensemble Statistical Forecasting System. This uses five predictors as mentioned below. The final LRF is given with the help of last 100 years data involving these predictors and with some equations. With the help of super computers, scientists carry out a statistical analysis to finally come out with a forecast.
| Predictor | Period |
|
The Sea Surface Temperature (SST) Gradient between North Atlantic and North Pacific
|
December + January
|
|
Equatorial South Indian Ocean SST
|
February
|
|
East Asia Mean Sea Level Pressure
|
February + March
|
|
Northwest Europe Land Surface Air Temperature
|
January
|
| Equatorial Pacific Warm Water Volume | February + March |
Rainfall category during Monsoon
|
Deficient
|
Less than 90% |
|
Below Normal
|
90 – 96%
|
|
Normal
|
96-104 %
|
|
Above Normal
|
104 – 110%
|
|
Excess
|
Above 110%
|





